Understanding Atrial Fibrillation and Its Medication Needs
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a prevalent heart rhythm disorder characterized by rapid and irregular beating. It affects millions worldwide, leading to complications such as stroke and heart failure if left unmanaged. Understanding the nature of AF is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. The heart’s upper chambers (atria) quiver instead of beating effectively, which can cause blood clots to form. These clots can travel to the brain, resulting in a stroke.
Medications play a pivotal role in the management of atrial fibrillation. They are used to control heart rate, restore normal rhythm, and prevent blood clots. Commonly prescribed drugs include anticoagulants, beta-blockers, and antiarrhythmic medications. The choice of medication depends on various factors, including the patient’s health status, the severity of symptoms, and the presence of other medical conditions.
It is essential for patients to adhere to prescribed treatments and maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. Regular monitoring and adjustments to medication may be necessary to ensure optimal management of the condition. Patients should be aware of potential side effects and interactions with other drugs, as these can significantly impact treatment efficacy and safety.
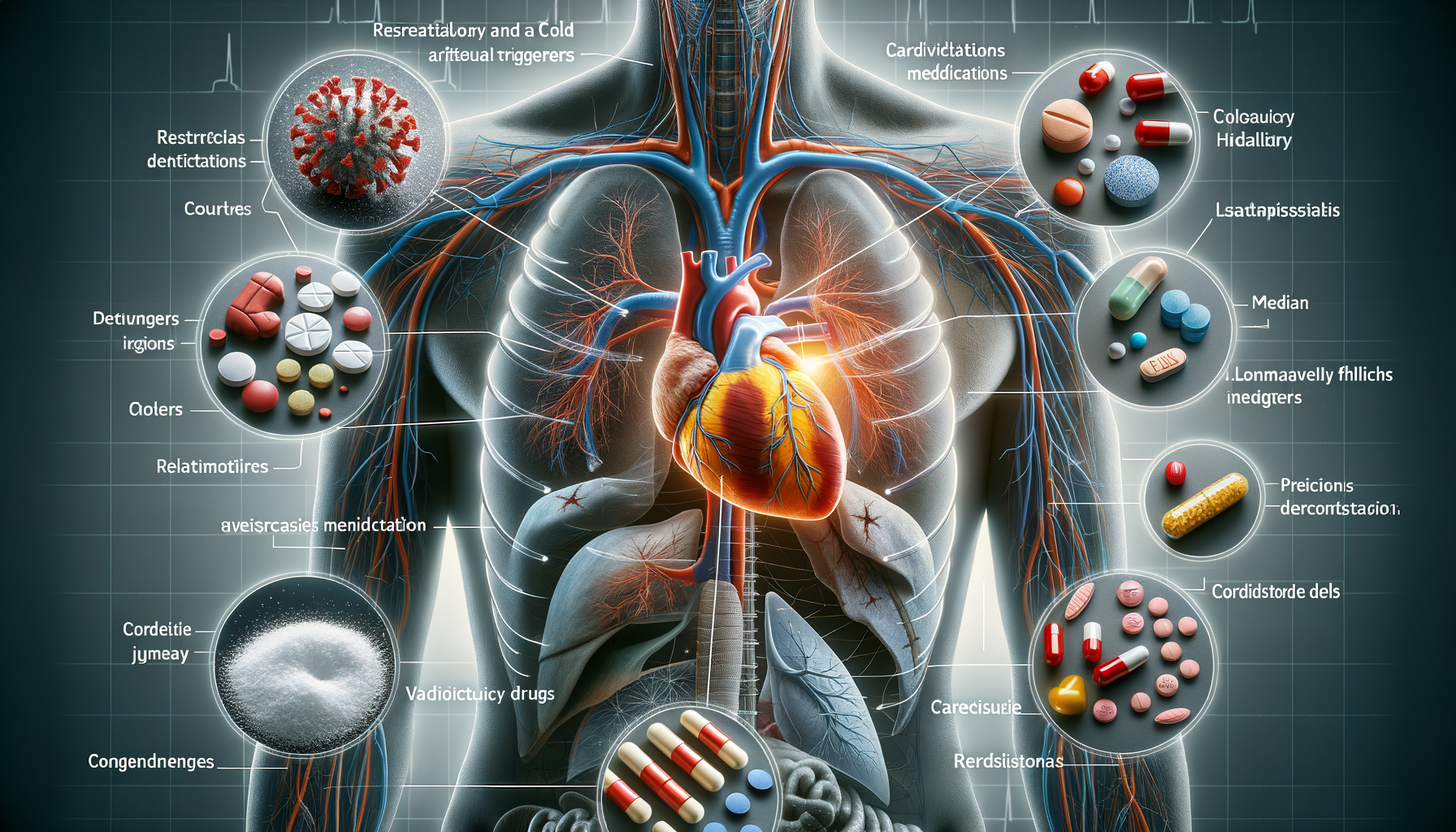
Respiratory and Cold Medications as Potential Triggers
Respiratory and cold medications, often used for common ailments like colds and allergies, can sometimes trigger or exacerbate atrial fibrillation. Many over-the-counter (OTC) cold remedies contain stimulants such as pseudoephedrine, which can increase heart rate and potentially provoke AF episodes.
These medications work by constricting blood vessels to reduce nasal congestion, but this vasoconstriction can lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate. Patients with atrial fibrillation should exercise caution when using these medications and consider alternatives that do not contain stimulants. Consulting with a healthcare provider before using any new medication is advisable to prevent adverse effects.
Moreover, some medications for respiratory issues, like certain bronchodilators, can also have similar effects on heart rhythm. It’s crucial for patients to inform their healthcare providers about all medications they are taking, including OTC drugs and supplements, to avoid potential interactions that could trigger AF.
- Check labels for stimulants like pseudoephedrine.
- Consult healthcare providers for safe alternatives.
- Monitor for any changes in heart rhythm when starting new medications.
Cardiovascular Drugs and Their Paradoxical Effects
While cardiovascular drugs are essential in managing heart conditions, some may have paradoxical effects in patients with atrial fibrillation. For instance, certain antiarrhythmic drugs, although designed to stabilize heart rhythm, can sometimes lead to proarrhythmia, a condition where the medication itself induces arrhythmias.
Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are frequently used to manage AF by controlling heart rate. However, in some cases, they may cause bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate), which could complicate the patient’s condition. It’s a delicate balance that requires careful monitoring and, at times, adjustments in therapy.
Patients should be vigilant about any new or worsening symptoms and report them to their healthcare providers promptly. Regular follow-ups and ECG monitoring can help detect any adverse effects early, allowing for timely intervention.
- Be aware of potential proarrhythmic effects.
- Report any new symptoms to healthcare providers.
- Regular monitoring is crucial for safe medication use.
The Importance of Understanding Medication Effects
Understanding how medications can impact atrial fibrillation is critical for effective management of the condition. Patients must be proactive in learning about their prescribed drugs, including potential side effects and interactions with other medications. This knowledge empowers them to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating patients about their medications. They should provide clear instructions and discuss the rationale behind each prescribed drug. Open communication between patients and providers ensures that any concerns or questions are addressed promptly, fostering a collaborative approach to managing AF.
Additionally, patients should maintain an updated list of all medications they are taking and share it with every healthcare provider they visit. This practice helps prevent potential drug interactions and ensures that all aspects of their treatment plan are aligned.
- Educate yourself about your medications.
- Maintain open communication with healthcare providers.
- Keep an updated list of all medications.
Conclusion: Navigating Atrial Fibrillation and Medication Management
Managing atrial fibrillation requires a comprehensive understanding of how various medications can affect heart rhythm. By staying informed and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, patients can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. It is crucial to recognize potential triggers, such as certain respiratory and cardiovascular drugs, and to take proactive steps in avoiding them.
Ultimately, a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers is key to successful management of atrial fibrillation. Regular monitoring, adherence to prescribed treatments, and a willingness to discuss any concerns or changes in symptoms are essential components of this partnership. By taking these steps, patients can navigate the complexities of AF and work towards achieving better heart health.



Leave a Reply