Understanding Mycosis Fungoides: An Overview
Mycosis Fungoides is a rare form of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma that primarily affects the skin. It is a type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, meaning it originates from T-cells, a type of white blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. The condition can be challenging to diagnose in its early stages because its symptoms often mimic those of more common skin disorders, such as eczema or psoriasis. Recognizing the early signs of Mycosis Fungoides is essential for timely diagnosis and management, as this can significantly impact the course of the disease and the effectiveness of treatments.
The progression of Mycosis Fungoides is typically slow, and it can take years for the disease to advance through its various stages. Initially, it may present as a rash that can be easily mistaken for other benign skin conditions. However, as the disease progresses, more distinct and severe symptoms may develop, necessitating a more comprehensive medical evaluation and intervention. Understanding the different stages and their associated symptoms can help patients and healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment and management strategies.
Common Symptoms of Mycosis Fungoides
The symptoms of Mycosis Fungoides can vary widely depending on the stage of the disease. In the early stages, patients may notice patches of red, scaly skin that can be itchy and uncomfortable. These patches often appear in areas not typically exposed to the sun, such as the buttocks, thighs, or breasts. As the disease progresses, these patches can evolve into thicker plaques, which are raised lesions that may become more widespread and pronounced.
In more advanced stages, Mycosis Fungoides can lead to the development of tumors on the skin. These tumors can vary in size and may ulcerate, causing pain and discomfort. Additionally, the disease can spread beyond the skin to affect lymph nodes and internal organs, leading to systemic symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for effective management, as timely intervention can help slow the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s quality of life.
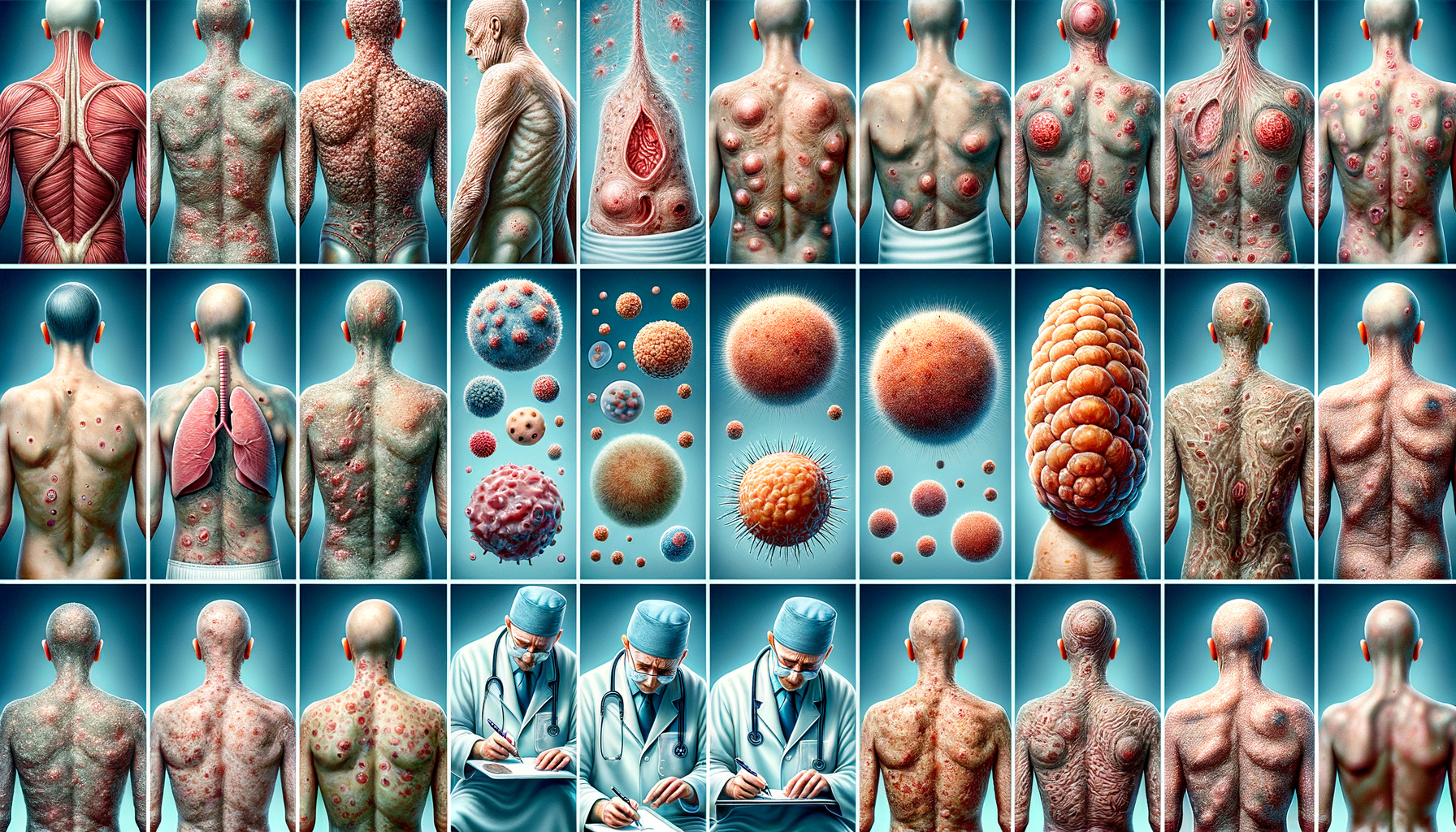
Visual Appearance Across Different Stages
Mycosis Fungoides progresses through several stages, each with distinct visual characteristics. In the early patch stage, the skin may exhibit flat, red, or pink patches that can be mistaken for eczema or psoriasis. These patches are often not itchy, which can delay diagnosis as they may not cause significant discomfort.
As the disease progresses to the plaque stage, the patches become thicker and more raised, forming plaques. These plaques are usually darker in color and may have a more defined border. They can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the trunk and extremities.
In the tumor stage, nodules or tumors develop on the skin. These can vary in size and may be painful or ulcerated. The tumors can be disfiguring and may lead to secondary infections. Recognizing these changes is vital for healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans accordingly and for patients to understand the seriousness of their condition.
Treatment Options and Clinical Approaches
The treatment of Mycosis Fungoides depends on the stage of the disease and the individual patient’s health status. In the early stages, treatment may focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression. Topical corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation and control itching. Phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light, can also be effective in treating patches and plaques.
As the disease progresses, more aggressive treatments may be necessary. These can include systemic therapies such as oral retinoids, which are vitamin A derivatives that help slow the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be considered in advanced cases where the disease has spread beyond the skin.
Clinical trials and new therapies are continually being explored to improve outcomes for patients with Mycosis Fungoides. Targeted therapies that focus on specific molecules involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells are showing promise in clinical research. Patients should discuss all available treatment options with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate approach for their specific situation.
Conclusion: Navigating Mycosis Fungoides
Mycosis Fungoides is a complex and challenging condition that requires careful management and monitoring. Early recognition of symptoms and understanding the progression of the disease are crucial for effective treatment. By staying informed about the latest treatment options and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can navigate the challenges of Mycosis Fungoides with greater confidence and hope.
While the journey with Mycosis Fungoides can be daunting, advancements in medical research and treatment strategies offer new avenues for managing the disease. Patients are encouraged to engage in open and ongoing discussions with their healthcare team to explore all available options and make informed decisions about their care.



Leave a Reply